Introduction:
In the quest for global electrification, remote and off-grid areas often find themselves in the dark. However, the dawn of innovative off-grid solutions is changing this narrative. This blog explores the basics of off-grid solutions, their genesis, the imperative need for their implementation, importance in the electrical field, recent advancements, practicality at a mass level, and an evaluation of their pros and cons.
I. Basics of Off-Grid Solutions:
Off-grid solutions refer to systems that generate and distribute electricity independently of a centralized power grid. These solutions are crucial for areas where traditional grid infrastructure is unavailable or economically unfeasible.
Off-grid solutions in electricity involve decentralized power systems, typically using renewable sources like solar or wind, to provide energy independently from the main electrical grid. These systems utilize energy storage, such as batteries, for power during non-generating periods. Off-grid setups are crucial for remote areas or locations with unreliable grid access, promoting self-sufficiency and reducing dependence on centralized infrastructure. The technology ensures continuous energy availability, fostering sustainability and resilience in diverse environments.
II. Genesis of Off-Grid Solutions:
The genesis of off-grid solutions lies in the recognition of the energy disparity faced by remote communities. Traditional grid expansion is often cost-prohibitive, leading to the development of decentralized and independent energy solutions tailored to the unique needs of off-grid areas.
III. Why Off-Grid Solutions are Needed:
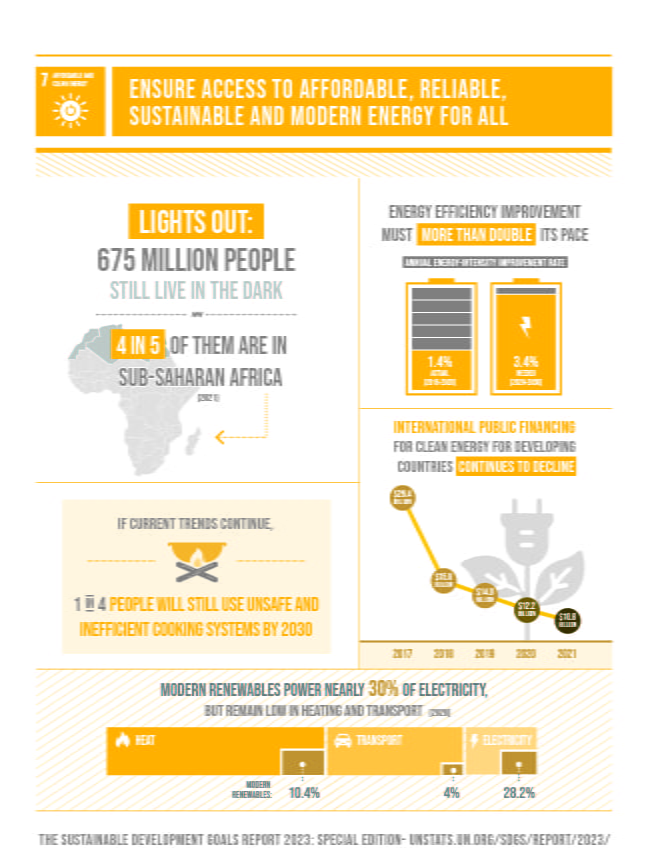
Energy Access:
Off-grid solutions address the pressing need for electricity in areas where grid extension is challenging or unaffordable.
Sustainable Development:
Access to electricity is a catalyst for sustainable development, empowering communities with opportunities for education, healthcare, and economic growth. Goal 7 of sustainable development louds for access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.
IV. Importance in the Electrical Field:
Decentralization:
Off-grid solutions contribute to the decentralization of energy production, reducing dependence on centralized power plants.
Renewable Energy Integration:
Many off-grid solutions leverage renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro, promoting a cleaner and sustainable energy mix.
V. Recent Advancements:
Solar Home Systems:
Advances in solar technology have led to affordable and efficient solar home systems that can power individual households.
Microgrids:
The development of smart and scalable microgrid solutions enables the creation of community-level energy networks, ensuring reliable power supply.
VI. Notable Examples:
M-KOPA Solar, Kenya:
M-KOPA provides pay-as-you-go solar solutions, allowing users to access affordable solar power and pay through mobile money.
Husk Power Systems, India:
Husk Power Systems converts rice husks into electricity, providing clean energy to rural areas in India.
VII. Practicality of Implementation at Mass Level:
Modular Systems:
Off-grid solutions often employ modular systems that can be easily scaled to meet the increasing energy demands of growing communities.
Community Engagement:
Successful implementation involves community engagement, ensuring that solutions align with the specific needs and preferences of the local population.
VIII. Pros and Cons:
Pros:
Increased Energy Access: Off-grid solutions bring electricity to areas with no access to traditional power sources.
Sustainable Development: Fosters economic and social development in remote communities.
Environmental Benefits: Many off-grid solutions use renewable energy sources, reducing environmental impact.
Cons:
Initial Costs: Upfront costs for technology and infrastructure can be a barrier to implementation.
Maintenance Challenges: Remote locations may pose challenges for maintenance and repairs.
Limited Scalability: Some solutions may struggle to meet the growing energy needs of expanding communities.
Conclusion:
Off-grid solutions represent a beacon of hope for bringing electricity to the world’s remote areas, empowering communities and fostering sustainable development. As technology continues to advance, the scalability and efficiency of these solutions will improve, making them an integral part of the global effort to achieve universal energy access. While challenges persist, the potential benefits make off-grid solutions a vital component of a more inclusive and electrified future.
Also Read:
